Mastering The Art Of Bloom's Taxonomy: A Guide To The Verb Wheel
The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy is an essential tool for educators and learners alike, providing a structured approach to categorizing educational goals. By utilizing this dynamic wheel, teachers can craft lesson plans that foster critical thinking and encourage deeper learning. The verb wheel serves as a visual representation of Bloom's Taxonomy, which is a framework that organizes cognitive skills from basic recall to complex evaluation and creation.
Bloom's Taxonomy has been a cornerstone of educational psychology since its inception in 1956. It was developed by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues to promote higher forms of thinking in education, rather than just rote memorization. The taxonomy is divided into six hierarchical levels: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation. Each level represents a different depth of understanding, and the verb wheel helps educators select appropriate verbs for each level, ensuring that learning objectives are clear and measurable.
In today's rapidly evolving educational landscape, the verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy is more relevant than ever. It allows educators to create learning experiences that are both engaging and challenging, catering to a variety of learning styles and abilities. By incorporating verbs from the wheel into lesson plans, teachers can guide students through the cognitive process, helping them develop critical thinking skills that are essential in the 21st century. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the verb wheel and its application in educational settings, providing insights and practical tips for educators seeking to enhance their teaching strategies.
Read also:Impact Of Racist Text Messages On Black Students Posttrump Victory
Table of Contents
- What is Bloom's Taxonomy?
- The History of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Understanding the Verb Wheel
- How Does the Verb Wheel Work?
- Benefits of Using the Verb Wheel
- Creating Effective Learning Objectives
- How Can the Verb Wheel Enhance Teaching?
- Examples of Verb Wheel in Action
- How to Integrate the Verb Wheel?
- Common Misconceptions About Bloom's Taxonomy
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- External Resources
What is Bloom's Taxonomy?
Bloom's Taxonomy is a framework that categorizes educational goals into six hierarchical levels, designed to promote higher forms of thinking in education. Developed by Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues, the taxonomy aims to encourage educators to focus on all three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Each level of Bloom's Taxonomy represents a step in the cognitive process, from basic recall of information to the ability to evaluate and create new ideas.
Levels of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Knowledge: The ability to recall factual information.
- Comprehension: Understanding the meaning of information.
- Application: Using knowledge in new situations.
- Analysis: Breaking down information into parts to understand its structure.
- Synthesis: Combining information to form a new whole.
- Evaluation: Judging the value of information or ideas.
The History of Bloom's Taxonomy
The origins of Bloom's Taxonomy can be traced back to the mid-20th century when educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom and his team developed this framework to classify educational objectives. Initially, it was designed to facilitate a common language for educators to discuss and exchange learning objectives and assessments. Bloom's Taxonomy has undergone several revisions, with the most significant update occurring in 2001, which redefined the categories and incorporated a more dynamic approach to learning.
2001 Revision
The 2001 revision of Bloom's Taxonomy introduced a two-dimensional framework: the Knowledge Dimension and the Cognitive Process Dimension. This revision aimed to address the limitations of the original taxonomy by providing a more comprehensive structure for categorizing educational objectives. The updated taxonomy emphasizes the importance of critical thinking and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios.
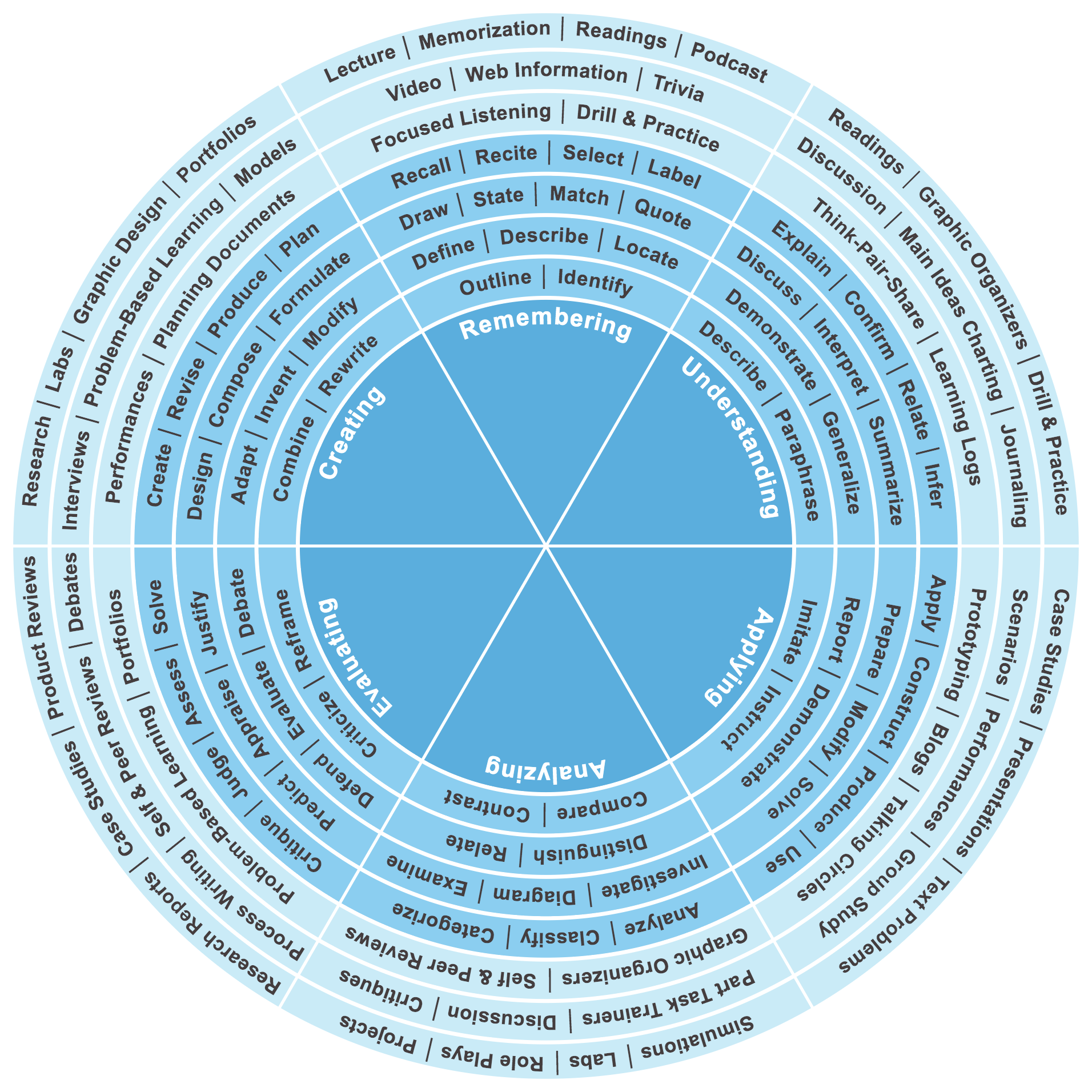
Understanding the Verb Wheel
The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy is a practical tool that helps educators select appropriate action verbs for each level of the taxonomy. These verbs are used to create clear and measurable learning objectives, ensuring that students understand what is expected of them at each stage of their learning journey. The verb wheel is organized into concentric circles, with each circle representing a different level of Bloom's Taxonomy and listing verbs that correspond to that level.
Components of the Verb Wheel
The verb wheel consists of several key components:
- Core: The center of the wheel represents the foundational level of Bloom's Taxonomy, Knowledge.
- Rings: Each subsequent ring corresponds to a higher level of the taxonomy, progressing from Comprehension to Evaluation.
- Verbs: Action verbs are listed within each ring, providing educators with a range of options for crafting learning objectives.
How Does the Verb Wheel Work?
The verb wheel functions as a guide for educators to develop learning objectives that align with Bloom's Taxonomy. By selecting verbs from the appropriate level of the wheel, teachers can ensure that their objectives are specific, measurable, and relevant to the desired cognitive outcome. The wheel serves as a visual aid, helping educators to easily identify verbs that correspond to each level of the taxonomy and apply them in their lesson plans.
Read also:Smart Pak Revolutionizing Convenience And Efficiency
Using the Verb Wheel in Lesson Planning
When planning a lesson, educators can use the verb wheel to choose verbs that match their learning goals. For example, if a teacher wants students to demonstrate their understanding of a concept, they might select verbs like "explain" or "summarize" from the Comprehension level. If the goal is to encourage critical thinking, verbs like "analyze" or "compare" from the Analysis level may be more appropriate.
Benefits of Using the Verb Wheel
Incorporating the verb wheel into educational practices offers numerous benefits for both educators and students. One of the primary advantages is the ability to create well-defined learning objectives that promote higher-order thinking skills. By using specific verbs associated with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy, teachers can design assessments and activities that challenge students to think critically and apply their knowledge in meaningful ways.
Enhanced Learning Outcomes
The use of the verb wheel leads to improved learning outcomes by encouraging students to engage with material at a deeper level. This approach fosters a more comprehensive understanding of concepts and allows students to develop skills that are essential for success in the modern world. Additionally, the verb wheel helps educators to differentiate instruction, catering to the diverse needs and abilities of their students.
Creating Effective Learning Objectives
Effective learning objectives are crucial to the success of any educational program. They provide a clear roadmap for both teachers and students, outlining what is expected and how achievement will be measured. The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy is an invaluable resource when crafting these objectives, as it ensures that they are aligned with the desired cognitive outcomes.
Steps to Creating Learning Objectives
- Identify the desired cognitive level: Determine which level of Bloom's Taxonomy aligns with your learning goals.
- Select appropriate verbs: Use the verb wheel to choose verbs that match the cognitive level and learning objectives.
- Write specific objectives: Craft objectives that are clear, concise, and measurable, using the selected verbs.
- Align activities and assessments: Ensure that classroom activities and assessments are designed to meet the learning objectives.
How Can the Verb Wheel Enhance Teaching?
The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy enhances teaching by providing a structured framework for lesson planning and assessment. It encourages educators to focus on developing higher-order thinking skills, which are essential for student success in an increasingly complex world. By incorporating the verb wheel into their teaching strategies, educators can create engaging and challenging learning experiences that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Encouraging Active Learning
Using the verb wheel in the classroom promotes active learning by encouraging students to participate in their education actively. This approach involves engaging students in activities that require them to apply, analyze, and evaluate information, rather than passively receiving knowledge. Active learning strategies, supported by the verb wheel, lead to improved retention and understanding of material, ultimately enhancing student achievement.
Examples of Verb Wheel in Action
To illustrate the practical application of the verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy, consider the following examples across various subjects:
Example 1: Science
In a science lesson on ecosystems, a teacher might use the verb wheel to develop objectives such as:
- "Describe the components of an ecosystem" (Comprehension)
- "Analyze the impact of human activities on ecosystems" (Analysis)
- "Design a conservation plan for a local ecosystem" (Synthesis)
Example 2: History
For a history lesson on the Civil Rights Movement, a teacher could create objectives like:
- "Explain the significance of key events in the Civil Rights Movement" (Comprehension)
- "Evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies used by civil rights activists" (Evaluation)
- "Create a multimedia presentation on a lesser-known civil rights leader" (Synthesis)
How to Integrate the Verb Wheel?
Integrating the verb wheel into your teaching practice requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some steps to help you effectively incorporate this tool into your lesson plans:
Steps for Integration
- Familiarize yourself with the verb wheel: Understand the structure and purpose of the wheel, and become comfortable using it in your planning.
- Plan lessons with the wheel in mind: Use the verb wheel to guide your selection of learning objectives and activities.
- Align assessments with objectives: Ensure that your assessments accurately measure the learning objectives you've set using the verb wheel.
- Reflect and adjust: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of your lessons and make adjustments as needed to improve student outcomes.
Common Misconceptions About Bloom's Taxonomy
Despite its widespread use, there are several misconceptions about Bloom's Taxonomy that can hinder its effective implementation in the classroom. One common misconception is that the levels of the taxonomy represent a strict hierarchy, where students must master one level before moving on to the next. In reality, learning is a dynamic process, and students may move between levels depending on the complexity of the material and their individual learning needs.
Clarifying Misconceptions
Another misconception is that Bloom's Taxonomy only applies to cognitive learning, neglecting the affective and psychomotor domains. While the taxonomy is primarily focused on cognitive skills, it is important to consider the emotional and physical aspects of learning when developing educational goals. By addressing these misconceptions, educators can use Bloom's Taxonomy more effectively to enhance student learning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy?
The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy serves as a tool for educators to create clear and measurable learning objectives that align with the cognitive levels of the taxonomy. It helps teachers select appropriate action verbs for each level, ensuring that students understand what is expected of them.
How does the verb wheel support differentiated instruction?
The verb wheel supports differentiated instruction by providing a range of verbs that cater to different cognitive levels and learning styles. This allows educators to tailor their teaching strategies to meet the diverse needs of their students, promoting a more inclusive and effective learning environment.
Can the verb wheel be used in all subject areas?
Yes, the verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy can be applied across all subject areas. By selecting appropriate verbs for each cognitive level, educators can create learning objectives and activities that are relevant to their specific subject matter.
Is Bloom's Taxonomy still relevant in modern education?
Yes, Bloom's Taxonomy remains a valuable framework in modern education. It provides a structured approach to developing critical thinking skills and fostering a deeper understanding of subject matter, which are essential for student success in the 21st century.
How can I assess student learning using Bloom's Taxonomy?
To assess student learning using Bloom's Taxonomy, educators should design assessments that align with the learning objectives created using the verb wheel. This ensures that assessments accurately measure the desired cognitive outcomes and provide valuable insights into student progress.
What are some challenges of implementing the verb wheel in the classroom?
Some challenges of implementing the verb wheel in the classroom include ensuring that learning objectives are appropriately aligned with cognitive levels and adapting the tool to meet the diverse needs of students. However, with careful planning and reflection, these challenges can be overcome to enhance student learning.
Conclusion
The verb wheel for Bloom's Taxonomy is a powerful tool for educators seeking to enhance their teaching strategies and promote higher-order thinking skills. By providing a structured framework for developing learning objectives, the verb wheel ensures that students are challenged and engaged in their education. As the educational landscape continues to evolve, the verb wheel remains a valuable resource for teachers looking to create meaningful and effective learning experiences.
External Resources
For further reading and resources on Bloom's Taxonomy and the verb wheel, consider exploring the following:
- Carnegie Mellon University's Teaching and Learning Principles
- TeachThought's Guide to Bloom's Taxonomy
- Edutopia's Deep Dive into Bloom's Taxonomy
Love Foundation Jenni: A Beacon Of Compassion And Hope
Decoding The Abbreviation: What "OFC Means" In Everyday Language
Gundam F90 Manga Raw: A Deep Dive Into Its Intricacies
Bloom's Taxonomy Wheel

Bloom's Taxonomy Bloom's Taxonomy Education